Stay safe during floods by monitoring official updates, having an emergency kit, and avoiding floodwaters. Prioritize your health by boiling water, cooking food thoroughly, and washing your hands often.
FloodSafety #EmergencyPreparedness #StaySafe #HealthFirst #DisasterReady #CommunitySafety
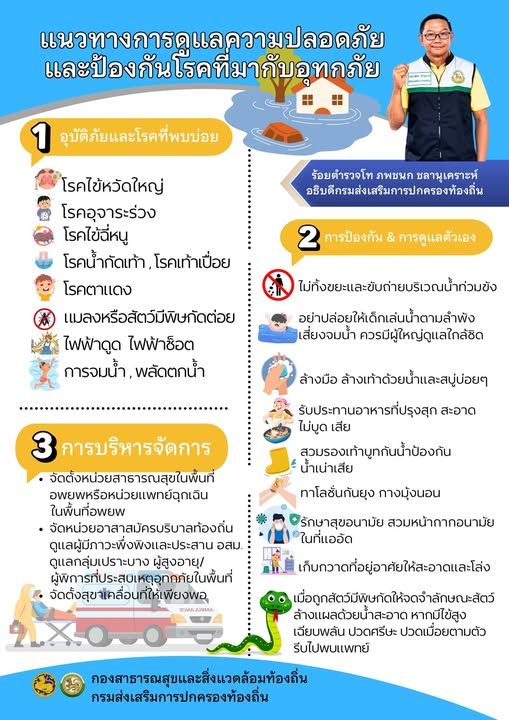
Floods are significant natural disasters with the potential to disrupt daily life, cause extensive property damage, and increase the risk of disease. Understanding how to stay safe and healthy during floods is essential for every household. The following structured guidelines cover vital safety steps and disease prevention measures to reduce risk during and after flood events.
Safety Measures During Floods
Monitoring Updates and Compliance
– Regularly monitor updates and alerts from official government agencies and local authorities.
– Adhere promptly to evacuation orders and other official instructions to avoid unnecessary risks.
Emergency Preparedness
– Prepare an emergency kit with necessary items, including prescription medicines, first aid supplies, non-perishable food, bottled water, flashlights, batteries, dry clothing, and communication devices like mobile phones and radios.
Electrical Safety
– Turn off electrical power at the main switch if water levels rise, especially before evacuating or if water threatens to enter living areas, to prevent electrocution.
Personal Movement and Transportation
– Avoid walking or wading through floodwaters as much as possible; submerged hazards and strong currents can be dangerous.
– Do not drive vehicles through flooded roads, as water depth and current strength can be deceptive and dangerous.
Preventing Diseases During and After Floods
Safe Drinking Water
– Consume only clean water. If unsure of water quality, boil it for at least one minute before drinking.
– Avoid using potentially contaminated water for cooking or brushing teeth.
Food Safety
– Eat only freshly prepared, thoroughly cooked meals.
– Discard any food that may have come into contact with floodwater.
– Avoid eating leftovers that are improperly stored or exposed to contamination.
Personal Hygiene
– Wash hands frequently with soap and clean water, especially before eating or after handling flood-affected items.
– If soap and water are unavailable, use alcohol-based hand sanitizers.
Protective Clothing
– Wear rubber boots or waterproof footwear to minimize contact with contaminated water and reduce the risk of diseases such as leptospirosis.
Vector Protection
– Use mosquito nets or apply insect repellent, particularly at night, to prevent mosquito-borne diseases like dengue fever and malaria.
Common Diseases to Watch for During Floods
Gastrointestinal Infections
– Waterborne diseases can include cholera, diarrhea, and dysentery due to the consumption of contaminated food or water.
Leptospirosis
– This bacterial infection is transmitted through contact with water contaminated by the urine of infected animals. It enters the body through cuts or abrasions in the skin.
Vector-Borne Illnesses
– Standing water provides breeding grounds for mosquitoes, increasing the risk of diseases such as dengue fever and malaria.
Skin Infections
– Prolonged exposure to floodwater can cause skin infections or aggravate existing skin conditions.
Recognizing Warning Signs and Seeking Medical Attention
Be alert for symptoms such as high fever, severe headache, muscle pain, persistent diarrhea, or abnormal urination. These may indicate serious infections or diseases contracted during floods. Seek medical attention promptly if any of these symptoms are present.
Additional Tips for Flood Recovery
- Disinfect and thoroughly clean all surfaces and household items that have been in contact with floodwater.
- Safely dispose of dead animals and debris to prevent further contamination.
- Monitor pets and livestock for signs of illness and limit their exposure to floodwater.
Staying informed, prepared, and vigilant are crucial aspects of safeguarding health and property during and after flood events. Implementing these guidelines significantly reduces the risks associated with floods.
Frequently Asked Questions
Flood Safety and Disease Prevention: Frequently Asked Questions
How can households best prepare for and respond to a flood emergency?
- Monitor updates from official agencies and local authorities.
- Promptly follow evacuation orders and official instructions.
- Prepare an emergency kit with first aid supplies, medications, non-perishable food, clean water, flashlights, batteries, and communication devices.
- Turn off electrical power at the main switch if floodwaters threaten your home.
- Avoid walking or driving through floodwaters.
What essential steps help prevent disease during and after floods?
- Drink only boiled or bottled water; avoid using water of uncertain quality for cooking or brushing teeth.
- Eat only freshly prepared, thoroughly cooked food. Discard any food that has come into contact with floodwater.
- Wash hands frequently with soap and clean water, especially before eating or after handling contaminated items.
- Wear protective clothing, such as rubber boots, to minimize direct contact with floodwaters.
- Use mosquito nets or repellent to guard against mosquito-borne illnesses.
What warning signs of illness should be watched for after a flood, and when should medical help be sought?
- Watch for symptoms like high fever, severe headache, muscle pain, persistent diarrhea, or unusual urination.
- These can signal serious infections such as leptospirosis, waterborne diseases, or mosquito-borne illnesses.
- Seek prompt medical attention if any of these symptoms occur to ensure proper diagnosis and treatment.